/ Monthly Market Update - September 2025
Humanoid robotics
The humanoid robots – science fiction or strategically important reality
Table of Contents
Insights
The current US-China trade war under President Trump’s second term differs significantly from the first trade war (2018-2020) in both scope and strategy, particularly with the central role of rare earth elements (REEs). During the first trade war, broad-based tariffs were implemented on China, aimed on reducing trade deficits and addressing intellectual property theft. The scope includes mainly consumer goods, industrial products, and agricultural exports. In the current trade war, rare earths are now a front-line strategic asset, with direct impact on defense, EVs, humanoids and clean energy. China had imposed export restrictions on seven heavy REEs and permanent magnets, while US responded with tariffs exceeding 100% at one point on China EVs, semiconductors, and AI-related products.
The humanoid robots – science fiction or strategically important reality?
Imagine a world where robots seamlessly blend into everyday life, mirroring human appearance and capabilities, augmenting our productivity, enriching experiences, and even providing emotional support. Welcome to the emerging era of Humanoid Robots, advanced machines designed to replicate human behaviour, physicality, and intelligence.
Humanoid robots have long been a staple of science fiction, but today, they are becoming a reality. With advancements in artificial intelligence, machine learning, and robotics engineering, humanoid robots are now capable of performing tasks once thought to be exclusive to humans. Humanoids are the next big thing in robotics: China, the world’s largest market for industrial robots, has set out specific targets for its plans to mass-produce humanoids. Meanwhile, tech companies in the US and Europe are announcing significant funding.
What are the trends, opportunities, and potential limitations of humanoids?
Let’s start with a definition - what are humanoid robots?
Humanoid robots represent the apex of robotics, combining advanced AI, mechanical engineering, and human-like appearance. Initially conceived as industrial and entertainment solutions, today’s humanoid robots are evolving rapidly, promising significant impacts across diverse industries and redefining the boundaries of human-machine collaboration.
Humanoid robots are machines that mimic human form and behaviour, they usually have:
- A human-like structure: Two arms, two legs, a torso, and a head.
- Advanced sensors and AI: Enabling them to see, hear, and interact.
- Mobility: Walking, running, and performing tasks like humans.
- Cognitive abilities: Decision-making, learning, and adapting to environments.
Humanoid robots are built using a combination of mechanical, electronic, and AI technologies to enable them to function in environments designed for humans. Currently, most humanoid robots operate with a mix of autonomy and human control. AI advancements are enabling them to become ever more self-sufficient. Humanoid robots learn through machine learning algorithms, real-world data processing, and continuous updates that improve their interactions with humans and the environment.
1. Key trends and developments on humanoid robots
Realistic Human Interaction: Enhanced artificial intelligence and natural language processing allow humanoid robots to engage in meaningful and emotional conversations with humans, significantly improving user acceptance and usability. Robots can now interpret gestures, facial expressions, and voice tone nuances to interact more naturally and effectively. And of course they can speak multiple languages!
Advanced Mobility and Dexterity: Innovations in robotic hardware, artificial muscles, actuators, and sensor technology have dramatically increased humanoid agility, allowing robots to move fluidly, manipulate objects precisely, and safely navigate dynamic environments. This engineering advancement enables their participation in increasingly diverse and challenging tasks.
Cognitive and Emotional Intelligence: The integration of emotion recognition systems and cognitive AI has equipped robots with unprecedented levels of empathy and adaptive learning, improving interactions and opening new roles for robots in sectors such as caregiving, education and customer service.
Collaborative Autonomy: Development in autonomous decision-making capabilities allows humanoid robots to perform tasks independently yet cooperatively alongside human coworkers, leading to increased productivity and safer work environments.
2. Practical and future use cases
Customer and Retail Service – Humanoid robots could transform retail by providing personalized assistance, managing inventory in real-time, and enhancing the overall shopping experience. They would interact naturally with customers, recognizing preferences, speaking multiple languages, processing transactions, and adapting responses, thus streamlining the shopping experience.
Healthcare and Elderly Care – Robots like “Pepper” (humanoid robot designed as a social companion for the home – created by Aldebaran Robotics and SoftBank) already assist with patient engagement. Future humanoid robots may provide comprehensive caregiving, supporting elderly and disabled individuals with daily tasks, medication reminders, physical therapy support, and emotional companionship. This would improve quality of life, reduce healthcare costs, address the global caregiving labour shortage and allow human healthcare workers to focus on more complex, empathetic aspects of patient care.
Education and Training – Humanoid robots are transforming the education sector by making learning more interactive and personalized. Their applications include:
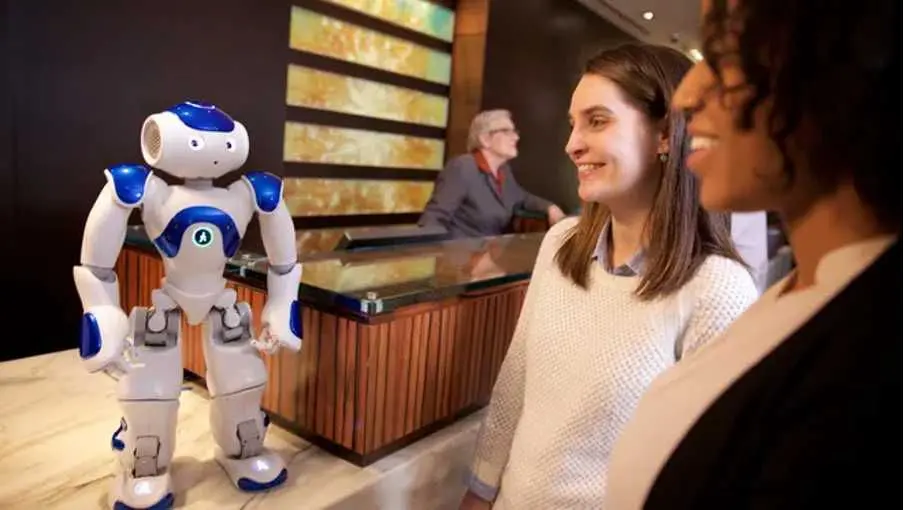
- Teaching assistants: Robots like NAO and Pepper help students understand complex subjects through interactive lessons.
- Special needs education: These robots assist children with learning disabilities by providing customized learning experiences.
- Language learning: AI-powered humanoid robots can help students practice new languages through real-time conversation.
Hospitality and Entertainment – In hospitality, robots can personalize guest experiences by remembering preferences and delivering consistently high-quality customer service.
Some examples include:
- Retail assistants: Robots guide customers to specific products, provide information about promotions, and even process payments.
- Hotel concierge services: Robots like Connie (Hilton’s AI concierge) and Henn-na Hotel’s robotic staff in Japan assist guests with check-ins, room services, and FAQs.
- Banking assistance: Banks are deploying humanoid robots to help customers with transactions and inquiries, reducing wait times.
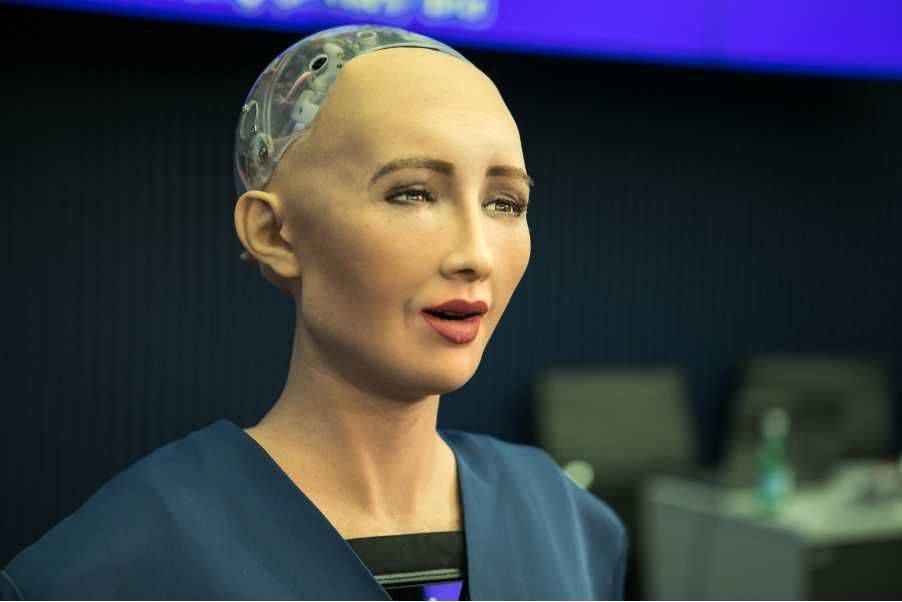
- Theme parks and exhibitions: Robots like Sophia from Hanson Robotics performs live interactions and demonstrations.
Image of Sophia, developed by Hanson Robotics used in entertainment – fun fact, Sophia has been granted “citizenship” by Saudi Arabia.
Source: ITU Pictures, CC BY 2.0, via Wikimedia Commons
NAO is a compact humanoid robot developed by Aldebaran Robotics (now part of SoftBank Robotics).
Source: IBM; https://prnewswire2-a.akamaihd.net/p/1893751/sp/189375100/
Emergency and Hazardous Environment Support – In industries where repetitive and physically demanding tasks are required, humanoid robots are improving efficiency and safety. Their contributions include:
- Factory automation: Robots assist in assembling products, conducting quality checks, and even handling logistics.
- Hazardous environment work: In places like nuclear plants and chemical factories, humanoid robots perform inspections and maintenance to minimize human risk.
- Another compelling use case is in disaster response. When earthquakes, floods, or industrial accidents occur, humanoid robots can be deployed to assess damage and perform rescue operations in environments too hazardous for human first responders. This capability was demonstrated during the 2011 Fukushima nuclear disaster, where robots (although not humanoid) were used to explore contaminated areas and assist in cleanup efforts.
Manufacturing – Advanced humanoid robots are not destined to replace human workers entirely. Instead, they are poised to revolutionize industries by complementing human skills and addressing critical labour shortages in hazardous environments.
- Unlike their predecessors, these machines are designed to navigate complex, human-centric environments with unprecedented dexterity and adaptability. This makes them ideal for tasks that were previously too dangerous or impractical for traditional robots.
- At automotive plants for example, these machines can work alongside human employees, handle heavy components and perform repetitive tasks with precision. This not only increases efficiency but also reduces the risk of injury to human workers.
Space Exploration – Humanoid robots play a crucial role in space missions where human presence is limited. They assist astronauts by:
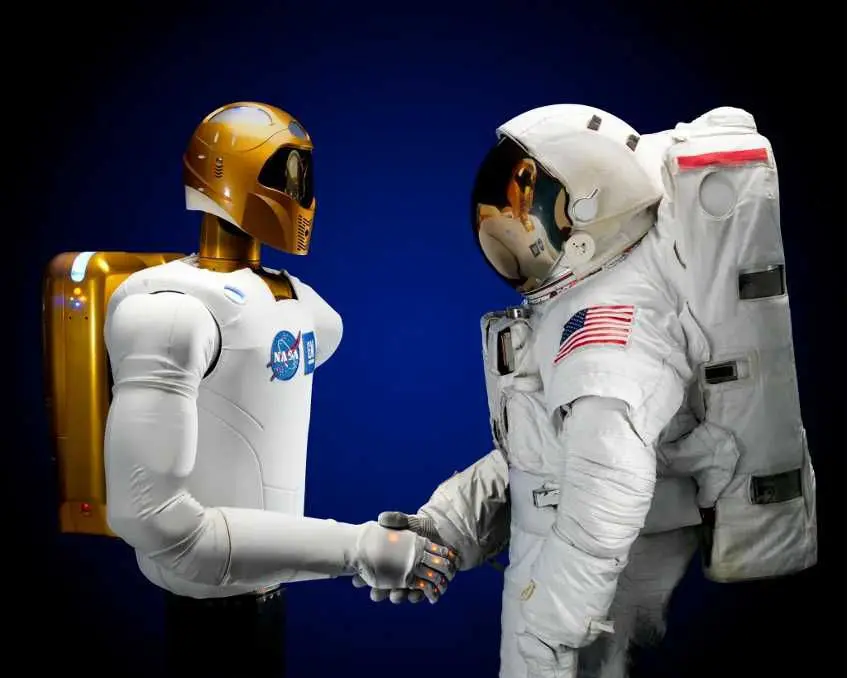
- Performing repairs: Robots like Robonaut 2 (developed by NASA) help with maintenance tasks on the International Space Station (ISS)
- Exploring extraterrestrial environments: Future missions aim to deploy humanoid robots on Mars to conduct research and to set up equipment before human arrival.
Picture of Robonaut 2 developed by NASA and General Motors to assist astronauts
Source: NASA; https://www.nasa.gov/wp-content/uploads/2015/04/471146main_jsc2010e089924_hi.jpg?w=1024
Military and Defense – The defense industry is leveraging humanoid robots for tactical and support roles. Large fundings usually come from governments when the application is related to the defense sector (US DoD and Chinese MIIT).
Examples of implementation include:
- Search operations: Robots assist in navigating dangerous terrains and war zones.
- Explosive ordnance disposal (EOD): Humanoid robots help in detecting and diffusing explosives safely.
- Training simulations: Military forces use humanoid robots to simulate realistic combat scenarios for training soldiers.
3. Leading players in humanoid robotics
Boston Dynamics: Renowned globally for their pioneering work in humanoid robotics, Boston Dynamics has created Atlas, one of the most advanced humanoid robots with exceptional agility and mobility. Atlas demonstrates impressive balance, dexterity, and coordination, capable of navigating complex environments and performing dynamic movements like parkour and dance routines, highlighting its potential for search-and-rescue and industrial applications.
Hanson Robotics – Hanson Robotics is recognized for developing Sophia. Sophia exemplifies highly realistic facial expressions, natural language processing, and engaging conversational skills, establishing new standards for human-robot social interaction. Hanson Robotics’ vision is deeply rooted in creating robots capable of understanding and empathizing with human emotions, thus bridging the gap between humans and machines.
SoftBank Robotics – Initial pioneer and creator of Pepper and NAO, SoftBank Robotics changed strategy and now specializes in robots for commercial use. Their robots are widely adopted in retail, healthcare, hospitality, and education sectors.
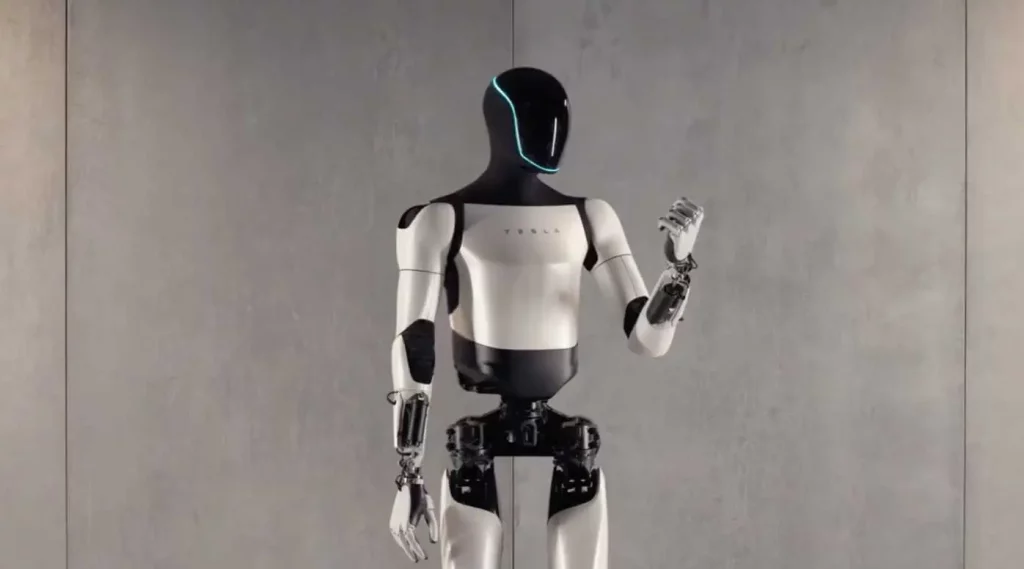
Tesla (Tesla Optimus) – Tesla has entered the humanoid robotics space ambitiously with Optimus, aiming for mass production and affordability. Optimus is designed to handle repetitive, unsafe, or physically demanding tasks, potentially revolutionizing factories, warehouses, and even homes by significantly augmenting human productivity and safety standards.
Unitree Robotics – Unitree Robotics is known for their highly dynamic and affordable humanoid and quadrupedal robots designed for research, education, and commercial usage. Unitree robots G1 and R1 demonstrate impressive agility, speed, and robustness, allowing exploration of complex human-robot collaborative scenarios, particularly in academia and applied industrial contexts.
4. Challenges in Humanoid Robotics
Despite advancements, humanoid robots face several challenges:
High Cost of Development – Building humanoid robots involves cutting-edge AI, mechanical engineering, and sensors, making them expensive. There is not yet a mass production reaching economies of scale regarding costs. Having said that, Elon Musk has stated in 2024, that the Tesla Optimus humanoid robot is expected to cost between $20,000 and $30,000 when it reaches commercial production. Additionally, Unitree is boasting a price as low as $6,000 for its R1 model.
Energy Consumption and Efficiency – Humanoid robots require high power consumption for their movement and AI processing. Consequently, the battery providers (Samsung SDI or CATL for example) are working hard to create batteries that would last longer, be smaller/lighter and optimise energy consumption. Now batteries do not last a full working day.
AI Limitations – While AI has advanced, humanoid robots still struggle with natural human interaction and decision-making.
Ethical and Social Concerns – There is a debate on how humanoid robots should be integrated into society. Concerns regarding job displacement and privacy issues arise with their implementation. As we integrate humanoid robots into our industries, striking a balance between technological advancement and workforce considerations is crucial. This requires a multifaceted approach combining retraining programs, gradual deployment, collaborative design, and ethical guidelines. Here we have many examples of dystopian movies to alert us to the importance of controlling the development of such humanoid robots in the society (here the “terminator” movies and Skynet come to my mind!).
5. Final thoughts
Humanoid robots are no longer just a concept. While challenges remain, as technology advances, these robots will improve in intelligence, dexterity, and usefulness, paving the way for a world where humans and robots coexist seamlessly.
Despite the advanced capabilities of humanoid robots, there will always be a need for human oversight and intervention.
For instance, in a manufacturing setting, humanoid robots might handle the physical assembly of products, while human workers focus on quality control, process improvement, and customer interaction. This symbiotic relationship allows for increased productivity while maintaining the flexibility and problem-solving capabilities that humans excel at.
6. What is the Humanoid robot’s investment universe?
After years of American companies like Boston Dynamics Inc. leading the development of humanoid robots, Chinese start-ups are now pushing the boundaries of innovation.
On an April 2025 conference call, the billionaire Elon Musk said he thinks his Optimus robots lead the industry in performance, but China may end up dominating the field. “I’m a little concerned that on the leaderboard, ranks 2 through 10 will be Chinese companies,” he said.
Citigroup Inc. recently projected the market for the machines and related services will surge to $7 trillion by 2050 when the world could be populated by 648 million human-like bots.
China, which already has a higher density of robots per human on its factory floors than the likes of the US and Japan, is preparing humanoids to move into increasingly complex roles. Unitree and its competitors have started trials for everything from sorting garbage and delivering medicines in nursing homes to patrolling the streets alongside police officers and guiding tours through museums.
China announced earlier this year it would invest 1 trillion yuan ($138 billion) in robotics and high tech in the next two decades, far more than the US or Europe.
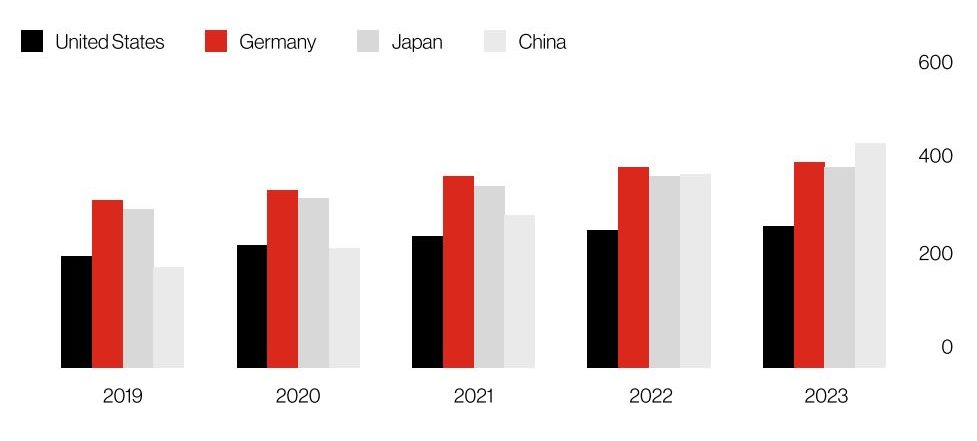
China has increased the use of factory robots to 470 per 10,000 workers – Source: International Federation of Robots
Therefore, it comes as no surprise that a lot of American and Chinese companies are important in this strategic sector.
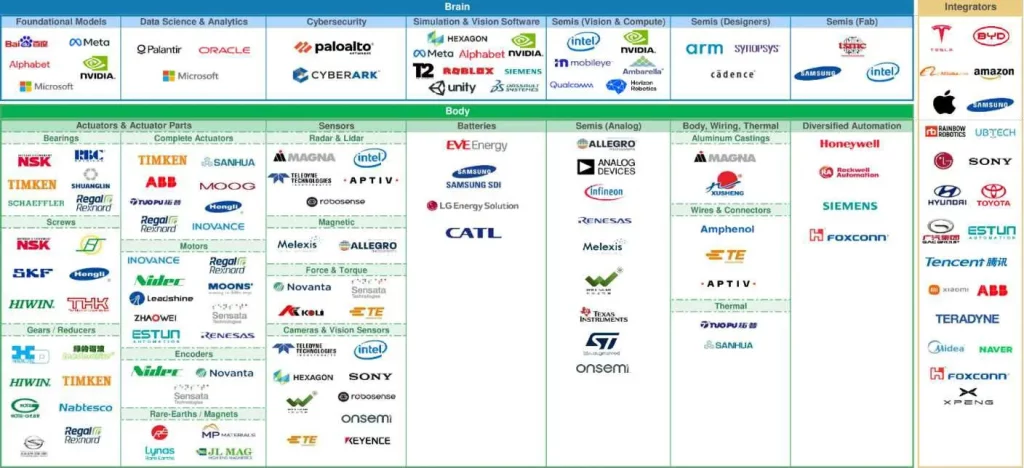
Below you can see the listed companies involved in the humanoid robot’s creation from supplier of parts (sensors, mechanical parts, chips, etc…) to integrators (those assembling the robots).
The Humanoid 100: Morgan Stanley’s List of Global Humanoid Enablers
Sources :
https://digitopia.co/blog/future-of-humanoid-robots/
https://thinkrobotics.com/blogs/learn/humanoid-robots-the-future-of-human-like-machines
International Federation of Robotics – https://ifr.org/
Bloomberg News
Morgan Stanley – the Humanoid 100
Disclaimer
The documents herein are issued for general information purposes only. Views and opinions contained herein are those of Bordier & Cie. Its contents may not be reproduced or redistributed. The user will be held fully liable for any unauthorised reproduction or circulation of any document herein, which may give rise to legal proceedings. All information contained herein does not constitute any investment recommendation or legal or tax advice and is provided for information purposes only. Please refer to the provisions of the legal information/disclaimer page of this website and note that they are fully applicable to any document herein, including and not limited to provisions concerning the restrictions arising from different national laws and regulations. Consequently, Bordier & Cie does not provide any investment service or advice to US persons as defined by the regulations of the US Securities and Exchange Commission, thus the information herein is by no means directed to such persons or entities. © 2025 Bordier Group and/or its affiliates.